Energy-Saving Myths Busted: Discover the Shocking Truth About What Really Works!
When it comes to cutting down utility bills, most people rely on what they’ve heard — but many of those so-called facts are actually energy-saving myths.
Energy‑Saving Myths Debunked
Every homeowner has heard them: leave the TV on overnight, wrap your water heater, unplug chargers to save power. These energy‑saving myths circulate because they sound logical—but many are misguided. This comprehensive guide explores and debunks these myths using real data and expert insight, so you can focus on strategies that truly work. From household appliances to whole‑home upgrades, you’ll learn where to invest your time and money, and which so‑called energy tricks are just a waste. Ready to uncover the truth versus the hype? Let’s begin.
Myth: Lowering the Thermostat Saves More Than Reducing Water Heat
One of the most common energy-saving myths is that simply lowering your thermostat yields massive cost reductions. While it’s true that every degree down saves about 1–3% on your heating bill, the myth exaggerates its effectiveness. In reality, you’ll see greater savings by tackling home efficiency holistically—such as insulating your attic, sealing air leaks, and upgrading old HVAC systems. These strategies reduce heat loss far more effectively than minor thermostat tweaks. Don’t fall for the overhyped myth—real energy efficiency requires a broader strategy.
Myth: Close Vents in Unused Rooms to Save Energy
Among persistent energy-saving myths is the belief that closing vents in unused rooms can significantly cut costs. While the logic appears sound, this action disrupts the balance of airflow in your HVAC system. Increased duct pressure and poor airflow can make your system work harder, using more energy rather than less. Instead, use smart zoning or dampers to manage temperature in specific areas. Understanding airflow dynamics helps bust this widespread myth once and for all.
Myth: ENERGY STAR Always Guarantees Big Savings
ENERGY STAR is a trusted label—but another of the frequent energy-saving myths is assuming all ENERGY STAR products deliver the same level of efficiency. A certified TV may save only a few dollars annually, whereas an ENERGY STAR refrigerator or dishwasher can cut hundreds over time. Smart consumers dig deeper: read EnergyGuide labels and assess appliance use within your own home. Remember, some non-certified appliances optimized for your exact use case might perform better.
Myth: Ceiling Fans Cool the Room, Not People
Ceiling fans are often misunderstood, and one of the popular energy-saving myths is that they cool the room itself. They don’t—they create a wind-chill effect that cools people, not air. Leaving them on in empty rooms wastes electricity. Use ceiling fans strategically: turn them off when unoccupied and pair them with AC to distribute cool air more efficiently. This knowledge debunks yet another common myth.
Myth: Using Dark Paint Helps Heat Faster in Winter
This is one of the quirkier energy-saving myths: that dark-colored exteriors help warm your home in winter. While darker colors do absorb more heat, the gain is negligible compared to heat lost through walls, windows, and roofs. Your focus should be on thermal insulation, window upgrades, and air sealing. Don’t expect miracles from your paint job—it’s not a substitute for real energy-efficient solutions.
Myth: Block Vents to Redirect Air
Blocking vents is a repeat offender on energy-saving myths lists. Like closing them, blocking vents can cause pressure imbalances, duct damage, and reduced HVAC efficiency. Smart zoning systems and dampers are better alternatives to manage heating and cooling across rooms. In short, vent manipulation is more myth than method.
Myth: Pool Covers Only Conserve Water—Not Energy
Contrary to one of the lesser-known energy-saving myths, pool covers actually do more than save water. They retain heat by preventing evaporative cooling overnight, especially in heated pools. A pool cover can reduce heating costs significantly, preserving both energy and water resources. Unlike many myths, this one’s actually grounded in truth.
Myth: LED Lights Need Warm-Up Time
A relic from the CFL era, the myth that LEDs require warm-up time still lingers. Modern LEDs reach full brightness instantly and consume a fraction of the energy of traditional bulbs. These lights bust one of the outdated energy-saving myths while also offering longer lifespan, low heat output, and reduced environmental impact.
Myth: Bigger HVAC Units Save Energy
Another damaging entry in the list of energy-saving myths is the belief that bigger HVAC systems are better. Oversized units frequently cycle on and off, consuming more energy and wearing out faster. Proper sizing based on Manual J calculations ensures consistent comfort and optimized energy use. Bigger isn’t always better—it’s just one of many myths that oversimplify home efficiency.
Myth: Washing Clothes in Cold Water Doesn’t Clean Them
Many still believe cold water can’t clean clothes effectively—yet another myth. With today’s advanced detergents, cold water removes dirt and stains just as well on most loads. It also preserves fabric quality and reduces energy use by up to 90% compared to hot cycles. This simple change challenges one of the oldest energy-saving myths in laundry routines.
Myth: Closing Shade Curtains Increases AC Efficiency
A myth rooted in partial truth, closing curtains only helps if they truly block sunlight. Sheer or lightweight curtains may trap heat between the fabric and window, worsening the effect. To bust this myth, invest in reflective blinds, blackout curtains, or thermal shades. These materials actually prevent solar gain and make a real impact on AC efficiency.
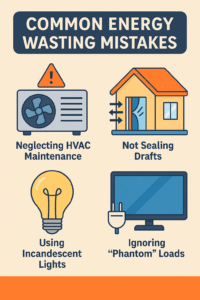
Myth: Unplug Everything at Night to Save Energy
Manually unplugging devices nightly is not only inconvenient—it’s an overestimated solution. One of the modern solutions to this old-school myth is using smart power strips. They cut phantom loads automatically when devices go into standby mode. Busted myth, better solution, improved efficiency.
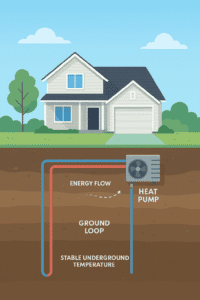
Myth: Solar Panels Don’t Work in Cloudy Weather
One of the most misleading energy-saving myths is that solar panels only work on sunny days. In fact, they can still produce 75–90% of their output on overcast days and are highly effective in winter with reflective snow or bright clouds. Modern systems are optimized for varied climates, busting this common misconception.
Myth: Programmable Thermostats Save Energy Automatically
Another widespread myth is that simply installing a programmable thermostat guarantees savings. That’s not entirely true. If not set correctly, programmable thermostats can underperform. Smart thermostats, on the other hand, adapt to your schedule, occupancy, and behavior, truly maximizing energy efficiency. This upgrade busts one of the most common energy-saving myths today.
Myth: Caulk Alone Seals All Gaps
Using caulk for sealing may seem like a one-size-fits-all solution, but relying solely on it is another energy-saving myth. Caulk degrades over time. Effective air sealing requires a multi-layered approach—spray foam, weather stripping, and pressure testing. Believing in caulk alone is a costly shortcut rooted in myth, not fact.
Myth: Standing Pilot Lights Are Efficient
Older appliances with standing pilot lights consume gas continuously, even when not in use. Newer systems with electronic ignition save about 25% in gas usage. Replacing standing pilot systems is a smart move and busts yet another gas-related energy-saving myth.
Myth: Turning Off HVAC Completely Saves More Than Setbacks
While it seems cost-effective to turn off HVAC when leaving the house, doing so forces it to work harder later. A setback strategy—reducing the temperature by a few degrees—is far more efficient. Smart thermostats make this even easier and help challenge energy-saving myths tied to outdated habits.
Myth: Washing Full Loads Is Always Efficient
Running full loads is smart—but only to a point. Overstuffing appliances reduces efficiency and leads to poor cleaning. Use your appliance’s eco-mode and follow manufacturer load recommendations to get real savings. Overloading is a myth that defeats the purpose of high-efficiency machines.
Myth: Dishwashers Use More Energy Than Hand Washing
One of the most surprising energy-saving myths is that hand-washing dishes saves energy. Modern dishwashers, especially ENERGY STAR-rated ones, use as little as three gallons per cycle—far less than a full sink of hot water. Just load efficiently and skip pre-rinsing to maximize efficiency and bust the hand-washing myth.
Final Thoughts: Focus on What Actually Works and not on Energy-saving myths
Busting these common energy-saving myths helps you cut through misinformation. Focus on proven strategies: upgrade to efficient appliances, seal and insulate your home, and use smart thermostats and routines. Small adjustments aligned with science-backed methods yield the best results. Don’t fall for claims that sound savvy—invest in changes that actually make a difference.
✅ Next Steps to Maximize Energy Savings:
- Conduct a home energy audit to identify key inefficiencies.
- Install a smart thermostat to automate savings.
- Upgrade insulation, seal leaks, and use efficient lighting.
- Replace appliances with Energy‑Star models.
This post was on Energy‑Saving Myths Busted: What Really Works.
Suggested Reads:
- Best Insulation Materials for Energy Savings in 2025
- The Ultimate Guide to Home Energy Efficiency in 2025
- Top 10 Smart Gadgets for Energy Efficiency in 2025
- Solar Panels vs Solar Roofs: Which is Better for Your Home?
Did you like the Energy-Saving Myths Busted Post? Let us know in the comments.